I did some network monitoring using performance monitor buildin in Win Srv and perform this monitor on hyper-v host on which VM with backup software is hosted. We use 1Gb network card for backups and as You can see below the max value was 122 482 913 Bytes sec which is about 976 Mbps (so about 1 Gbps). Network-related complaints top the chart in most application environments. There is always the blame game between whether it's a network issue or the application issue. Network congestions, packet drops, or device failures could impact application performance and connectivity.
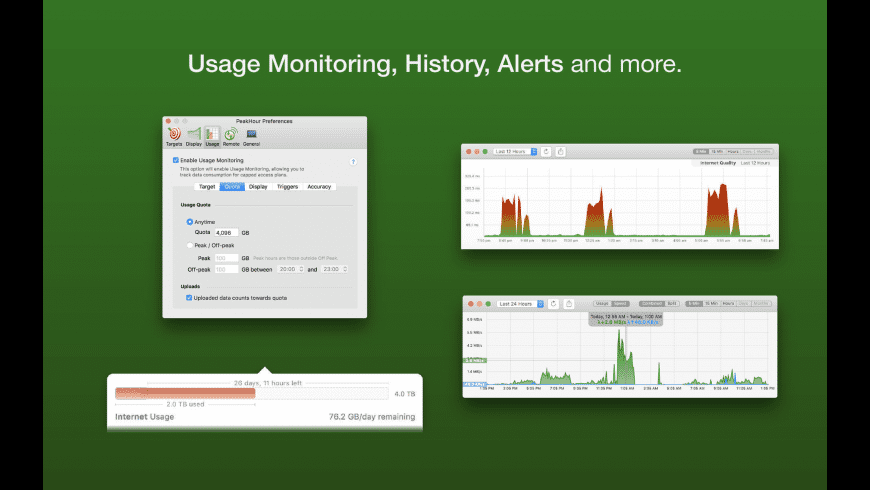
- Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 75
- Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 76
- Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 72
- Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 70
The sar stands for 'System Activity Report', which is used to collect, report or store system activity information.
It is a system performance monitoring command that is used to report various system performance metrics such as average CPU activity, individual CPU activity, memory used & available, device load, network, etc,.
The sar command is part of the sysstat package, which is not already installed on most Linux systems. Therefore, it can be installed using the associated distribution package manager.
If you want to get the average CPU or average memory usage report from the SAR report, go to the following article.
The sar command is one of the best tools for tracking historical system performance reports. Also, it allows you to investigate issues when you encounter performance problems on the system.
Peakhour 4 0 8 download free. By default it collects performance data for a week. This period can be extended beyond one month. If the value exceeds 28, the log files are placed in multiple directories, one for each month.
To do so, make the changes in the /etc/sysconfig/sysstat file. Edit the sysstat file and change HISTORY=7 to HISTORY=XX.
The sar data files are located in the /var/log/sa directory by default. All data are captured in binary form and saved to a file (datafile).
The data files are named saDD or saYYYYMMDD, where YYYY stands for the current year, MM for the current month and DD for the current day.
The data can then be selectively displayed with the sar command using the -f https://coolnfile740.weebly.com/timbuktu-pro-8-8-5.html. option. The sar command reports system-wide statistics, if you doesn't use -P flag.
SAR Command Store the below statistics:
- Average & Individual CPU utilization, it shows percentage of CPU utilization by user level (application) and system level (kernel).
- Total number of read/write requests issued to physical devices
- Total amount of data read from the devices and written to devices in blocks.
- Number of sectors read from the device and written to the device
- Total number of packets, compressed packets, network packets, TCP packets, UDP packets, and kilobytes received and transmitted
- Total number of bad and good packets received
- Amount of free, used, buffers, and cache memory in kilobytes.
- Percentage of used memory & swap space.
- Amount of used & free swap space in kilobytes.
- Percentage of time spent by the CPU for hardware interrupts, software interrupts, and virtual processor.
- Percentage of time that the CPU were idle.
sadc:sadc stands for 'system activity data collector'. It's a backend tool that collects the data collection for sar.sadf:It can generate sar report in CSV, XML, and various other formats. This will help you to integrate the sar report with other tools.
How To Install sysstat in Linux
The sysstat package is available in all Linux distribution repositories and can be easily installed with the help of the package manager.
For Fedora system, use DNF Command to install sysstat.
For Debian/Ubuntu systems, use APT-GET Command or APT Command to install sysstat.
For Arch Linux based systems, use Pacman Command to install sysstat.
For RHEL/CentOS systems, use YUM Command to install sysstat.
For openSUSE Leap system, use Zypper Command to install sysstat.
The sar data file is located in the below location on RHEL based systems such as Red Hat, Fedora and CentOS.
The sar data file is located in the below location on Debian based systems such as Debian, Ubuntu and LinuxMint.
The sysstat config file is located in the below location on RHEL based systems such as Red Hat, Fedora and CentOS.
The sysstat config file is located in the below location on Debian based systems such as Debian, Ubuntu and LinuxMint. Also, set ENABLED to true.
By default, it drops a cronjob file for sysstat in the below location and it will run every 10 minutes to collects sar data for historical reference. Directv now for pc download.
Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 75
/usr/lib64/sa/sa1 1 1:This cron job runs every 10 minutes and collects 1 report with 1 second interval. It can't be viewable by a text editor./usr/lib64/sa/sa2 -A:This cron job runs every day midnight (at 23:53) to create the daily summary report of the sar data. It can be viewable by a text editor. Also, it purges the data older than a particular number of days.
1) How to Check the CPU Usage Report of the System Using the sar Command
The below sar command shows today's CPU report statistics. This is the average of all CPUs.
Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 76
It shows the percentage of CPU utilization for user application, nice priority and system application.
Furthermore, it shows the percentage of time that the CPU were idle with outstanding disk I/O request and without any outstanding disk I/O request.
2) How to Check the System's Memory Usage Report Using the sar Command
The below sar command shows today's Memory report statistics for the system.
It shows the amount of free and available memory in kilobytes, amount of memory used as buffers and cache data by the kernel, amount of memory & percentage of memory needed for current workload, and percentage of used memory.
3) How to Check the System's CPU Usage Report Only for 3 Times with 1 Second Interval Using sar Command
The below sar command shows the system's CPU report statistics only for 3 times with one second interval.
4) How to Check the Individual Usage Report of Each CPU of the System Using the sar Command

The data can then be selectively displayed with the sar command using the -f https://coolnfile740.weebly.com/timbuktu-pro-8-8-5.html. option. The sar command reports system-wide statistics, if you doesn't use -P flag.
SAR Command Store the below statistics:
- Average & Individual CPU utilization, it shows percentage of CPU utilization by user level (application) and system level (kernel).
- Total number of read/write requests issued to physical devices
- Total amount of data read from the devices and written to devices in blocks.
- Number of sectors read from the device and written to the device
- Total number of packets, compressed packets, network packets, TCP packets, UDP packets, and kilobytes received and transmitted
- Total number of bad and good packets received
- Amount of free, used, buffers, and cache memory in kilobytes.
- Percentage of used memory & swap space.
- Amount of used & free swap space in kilobytes.
- Percentage of time spent by the CPU for hardware interrupts, software interrupts, and virtual processor.
- Percentage of time that the CPU were idle.
sadc:sadc stands for 'system activity data collector'. It's a backend tool that collects the data collection for sar.sadf:It can generate sar report in CSV, XML, and various other formats. This will help you to integrate the sar report with other tools.
How To Install sysstat in Linux
The sysstat package is available in all Linux distribution repositories and can be easily installed with the help of the package manager.
For Fedora system, use DNF Command to install sysstat.
For Debian/Ubuntu systems, use APT-GET Command or APT Command to install sysstat.
For Arch Linux based systems, use Pacman Command to install sysstat.
For RHEL/CentOS systems, use YUM Command to install sysstat.
For openSUSE Leap system, use Zypper Command to install sysstat.
The sar data file is located in the below location on RHEL based systems such as Red Hat, Fedora and CentOS.
The sar data file is located in the below location on Debian based systems such as Debian, Ubuntu and LinuxMint.
The sysstat config file is located in the below location on RHEL based systems such as Red Hat, Fedora and CentOS.
The sysstat config file is located in the below location on Debian based systems such as Debian, Ubuntu and LinuxMint. Also, set ENABLED to true.
By default, it drops a cronjob file for sysstat in the below location and it will run every 10 minutes to collects sar data for historical reference. Directv now for pc download.
Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 75
/usr/lib64/sa/sa1 1 1:This cron job runs every 10 minutes and collects 1 report with 1 second interval. It can't be viewable by a text editor./usr/lib64/sa/sa2 -A:This cron job runs every day midnight (at 23:53) to create the daily summary report of the sar data. It can be viewable by a text editor. Also, it purges the data older than a particular number of days.
1) How to Check the CPU Usage Report of the System Using the sar Command
The below sar command shows today's CPU report statistics. This is the average of all CPUs.
Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 76
It shows the percentage of CPU utilization for user application, nice priority and system application.
Furthermore, it shows the percentage of time that the CPU were idle with outstanding disk I/O request and without any outstanding disk I/O request.
2) How to Check the System's Memory Usage Report Using the sar Command
The below sar command shows today's Memory report statistics for the system.
It shows the amount of free and available memory in kilobytes, amount of memory used as buffers and cache data by the kernel, amount of memory & percentage of memory needed for current workload, and percentage of used memory.
3) How to Check the System's CPU Usage Report Only for 3 Times with 1 Second Interval Using sar Command
The below sar command shows the system's CPU report statistics only for 3 times with one second interval.
4) How to Check the Individual Usage Report of Each CPU of the System Using the sar Command
It shows each individual CPU usage when using the -P flag with sar command.
5) How to Check the Usage of the Specific CPU of the System Using the sar Command
The below sar command shows the usage statistics of the specific CPU instead of all.
6) How to Check the System's CPU Usage Report with Additional Fields
The below sar command shows the output with few additional fields.
7) How to Check the System Swap Space Usage Report
The below sar command shows the usage statistics of swap space.
8) How to Check the System's Other Memory Statistic Usage Report
The below sar command shows the usage memory statistics report such as number of memory pages freed and cached by the system per second.
Also, it shows how much memory pages used as buffers.
9) How to Check the System's Paging Statistics Usage Report
It reports variety of paging statistics.
10) How to Check the Swapping Statistics Usage Report of the System
It shows the total number of swap pages the system brought in and brought out per second.
11) How to Check the System's Queue Length and Load Average Usage Report
It shows the number of tasks in queue and number of tasks in the task list.
Also, it shows the system load average for the past 1/5/15 mins.
12) How to Check the I/O and Transfer Rate Statistics Usage Report of the System
It reports many statistics about reading and writing requests against physical devices and blocks.
13) How to Check an Each Block Device Statistics Usage Report
It especially report only about block device statistics.
14) How to Check the System's Network Statistics Usage Report
Use the -n flag followed by network keywords to generate various of network statistics reports.
List of Keyword's available for Network Statistics:
DEV:Displays network devices vital statistics for eth0, eth1, etc.,EDEV:Display network device failure statisticsNFS:Displays NFS client activitiesNFSD:Displays NFS server activitiesSOCK:Displays sockets in use for IPv4IP:Displays IPv4 network trafficEIP:Displays IPv4 network errorsICMP:Displays ICMPv4 network trafficEICMP:Displays ICMPv4 network errorsTCP:Displays TCPv4 network trafficETCP:Displays TCPv4 network errorsUDP:Displays UDPv4 network trafficFor IPv6:Use the following keywords such as SOCK6, IP6, EIP6, ICMP6, UDP6 are for IPv6ALLThis displays all of the above information. The output will be very long.
15) How to Check All Statistical Reports in One Go
Use the -n flag with sar command to print all statistical reports in one page.
16) How to Check the Context Switches Statistics Usage Report of the System
It shows context switches statistics usage report.
17) How to Check the CPU Statistics Usage Report of the System for a Specified Date
Use the specific date data file followed by the -f flag as described in the below example to verify the old sar report.
Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 72
18) How to Check the Memory Statistics Usage Report of the System for a Specified Date
This is similar to the above, but it shows the memory statistics report instead of the CPU.
19) How to Check the System Activity Report for a Specified Time
Peak Hour 4 Network Performance Monitor 4 1 70
This is similar to the above, but it shows the requested statistical report from the specified time.
